How to Store Salt Long Term
This post may contain affiliate links. Read my full disclosure here.
Salt is critical for life. It has been valued throughout recorded history. We’ll share why and how to store salt long term, plus tips for storage and safety.

7 Reasons Why You Should Store Bulk Salt
- You use it and need it. Salt is used every day for cooking and seasoning.
- If you have animals or livestock, they need salt, too.
- It may be hard to obtain in a SHTF situation. It isn’t something you can grow or make.
- You don’t have to worry about it going bad if you store it well, and it can be stored pretty much anywhere in an airtight container.
- You can save money buying salt in bulk, especially on sale.
- Salt is used for food preservation, including curing meats, pickling and canning.
- It can be used for trading or as a barter item.
How much salt should I store?
Salt is a cornerstone for food storage. Store 10 to 40+ pounds of salt per person, per year. The larger amounts assume you will use salt for food preservation, curing, and/or canning.
You can keep as much salt as you want, because salt lasts forever. The salt you store could last longer than the container. It is more of a question how much space you have.
If you are stocking up, keep at least 20 pounds of food grade salt per adult. As noted, if you cure meats or are into canning or fermenting, a larger amount of salt is better. Don’t forget to stock up when salt is on sale.
How to Store Salt for Long Term Storage
- Buy bulk salt that does not include caking agents (25 to 50lbs+)
- Ensure you have supplies – buckets, Mylar etc., moisture absorbers, Sharpie Marker etc
- Label Mylar bags with date, amount and info about the salt
- Prepare sealer
- Transfer salt to Mylar bag
- Add moisture absorber(s) as needed
- Seal Mylar bags with sealer or iron
- Store sealed and labeled Mylar bags in 5gal bucket
- Seal and label food grade bucket, tote or bin.
- Store food grade bucket, tote or bin pretty much anywhere.
Types of salt
This article contains recommendations for table salt. There are many common types of salt, including: iodized salt, pickling salt, sea salt, rock salt, and Epsom salts, to name a few.
Iodized salt is the most common table salt in many areas. It’s refined, and has added sodium iodide or potassium iodide. Many people recommend iodized salt because iodine is needed by the body for many different functions.
We prefer natural sea salt, which has trace amounts of iodine, as well as many other minerals. I use nori, kombu, kelp, and other seaweed for extra iodine. We also avoid salt with caking agents.
Pickling salt is refined, but contains no iodine. I use either pickling salt or sea salt for canning and making salt water brine for fermenting. Iodized salt will turn your preserved foods dark.
Seasoned salts, such as Lawry’s seasoned salt, garlic salt, onion salt, celery salt, etc., do not last indefinitely. For instance, the recommended shelf life of Lawry’s seasoned salt is 450 days in its original container in a cool, dry location.

Our Salt Suggestions
During a disaster, even a pinch of salt will change the flavor of food. Salt also helps maintain electrolyte balance in the body.
We prefer sea salt, because has trace minerals and natural iodine. Our favorites are Celtic grey sea salt, Himalayan pink salt and Redmond real salt. Store up at least 2 seasons worth of your favorite pickling salt for food preservation.
Avoid purchasing salts with anti-caking agents for long term salt storage. Iodized salt is best used within 5 years.
The Morton website notes: “While salt itself has no expiration date, salt products that contain iodine or seasonings that contain other ingredients such as spices, colors and flavors can deteriorate over time.”
Use coupon code “COMMONSENSE” to get 10% off your order at Country Life Natural Foods. (Check bulk pricing on Redmond real salt at Country Life Natural Foods here.)
Salt Storage Questions and Answers
Pure salt will last indefinitely in a sealed airtight container. Once opened, it can absorb odors and moisture. Moisture causes clumping and makes the salt difficult to use, and odors may cause off flavors.
How to extend the shelf life of salt in the pantry.
Once you open a larger bag of salt, store the remainder in an air tight container. A cool, dry place is best, but the air tight contain is an absolute requirement. The salt will not go bad, BUT it can pick up bad flavors and moisture from the air.
Can I eat water softener salt?
Water softener salt is typically made with sodium chloride or potassium chloride, and other additives to prevent caking and mushing. It may cause stomach aches, and is not recommended for food or animals.
Can I eat rock salt?
Yes, if it is pure food grade rock salt. It might be gritty and you will likely need a grinder because the crystals are large. It is edible and the good news it doesn’t have any extra chemicals.
If it is de-icing rock salt (sidewalk salt), it probably has chemicals in it you cannot or should not eat.
Would you like to save this?
Why store salt in Mylar or a bucket?
Salt will last forever, but we still recommend you store salt in Mylar or at least a food grade bucket with moisture absorbers. It cuts down on the salt absorbing moisture and smells that could foul it.
What are the WRONG ways to store salt?
Don’t store salt unsealed, in paper or cardboard, in humid environments. Don’t store salt in metal containers in damp environment, because the salt can corrode the metal over time.
Salt is hydrostatic so it will absorb ANY water/moisture. It will suck up humidity in the air. It will also absorb other smells and some chemicals, so keep it sealed in a non-reactive container.
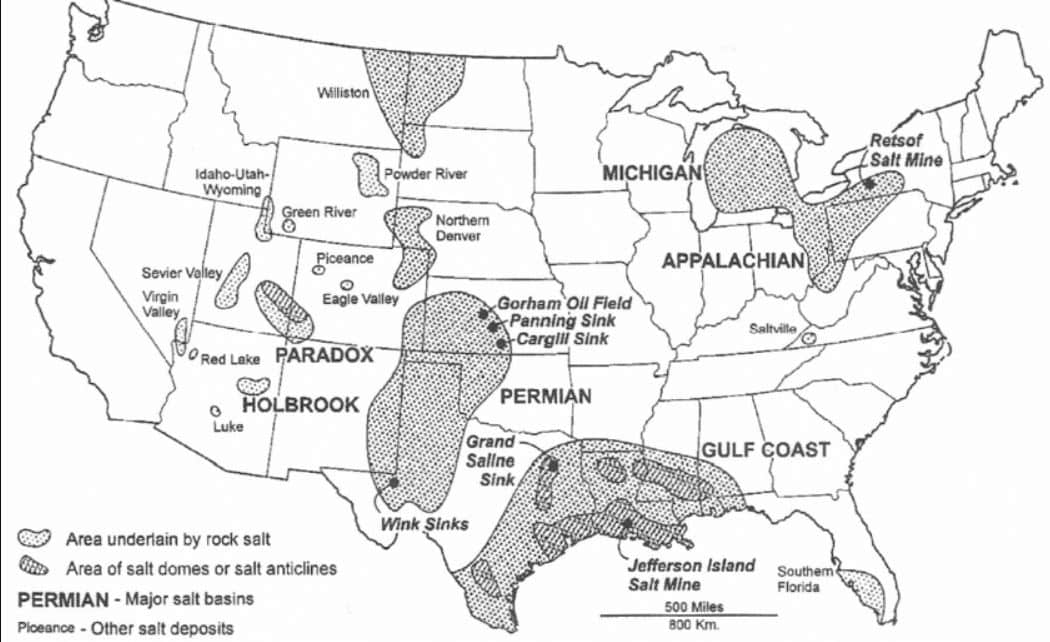
Where can you find salt?
There are salt deposits around the United States, but most requiring mining to access. You can also harvest salt from salt water, such as the oceans. This is a map of rock salt deposits from Johnson and Gonzales 1978.
Can you make salt from sea water?
Yes. If you evaporate salt water you get salt. Evaporating one liter (1000 mL) of seawater will give you about 35 grams of salts – or evaporate one gallon of seawater and you will get about 4.5 ounces of salt.
What are good containers for salt?
Store salt in canning jars, Mylar bags, food grade buckets, glass jars and sealed clay pots. Salt can interact with metal and some plastics, so choose containers meant for food storage. Canning jar lids may rust after long periods.
Can I store salt in plastic bags?
Yes, but we do not suggest storing salt in plastic bags for long term storage. A plastic bag may break open or tear, so something sturdier is better.
Plastic bags also break down (get brittle) as they age. If the bag fails, the salt can be spoiled by moisture and other contaminants.
Why use Mylar to store salt?
Mylar keeps moisture, chemicals and smells out.
We suggest five 1gal bags in a 5gal bucket. That way you open them in usable quantities. You can also use a single large 5gal Mylar bag to line to bucket.
Do you need oxygen absorbers to store salt long term?
No. You can add them if you like, but a moisture absorber is more practical. Use a Mylar bag and an appropriately sized moisture absorber. Or simply use a food grade bucket with an appropriately sized moisture absorber, or just a tightly sealed container.
Do you need a moisture absorber to store salt?
No, but moisture creates clumping, so the salt can become a challenge to use. If the moisture includes smells, it can foul the salt.
Why not just use the original packaging?
Salt will keep in the original packaging (paper or cardboard containers) but salt can absorb moisture creating clumps. Also salt can pick up smells that then change the flavor. The smells can “foul” the salt.
Mylar and food grade buckets keep out moisture and smells. You could also store the Mylar bags in a tote.
Does storage temperature affect shelf life of salt?
Salt is not temperature sensitive, so it can be stored in hot or cold areas, including a garage or outbuilding. You can store it in an attic, or outside in a tightly sealed container.



I admit knowing nothing about them, but what about the salts used for water softening? I see them in bulk bags at the local grocery. One would ‘think’ if they are used to treat water they are consumable?
As noted in the article, it’s not recommended because of the additives that are commonly included:
good article – only thing I’d add is about the weight involved – a 5 gallon bucket of salt or sugar will be the heaviest food bucket you’ll have – over 50 pounds >>> it’s a base bucket for sure ….. XXX
another reason to use an inner bag for bulk salt is the good possibility of the bottom bucket seam splitting open – there’s a 1/4″ indent that needs supporting on most of the buckets – piece of plywood glued down there can save the bucket integrity … XXX
in regard to bartering salt – prepare your barter size packages while you store for the long term >> the sandwich size ziplocks hold approx 1lb and re-use bread bags for the larger lots …
Great info to know. It helps learning from those who’ve already done the research. We have small children and are so busy it’s hard to find time to research these things. Thanks for sharing your knowledge with us.
Thank you, Sharon.